Let’s talk about the differences between these versions of AMD’s Ryzen processors and what those differences actually mean to you, the end user.
By the end of this article, you should have a solid idea of whether or not AMD Ryzen X3D CPUs are the right option for your next PC.
So let’s dive in!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
AMD Ryzen X3D vs X: What’s The Actual Difference?
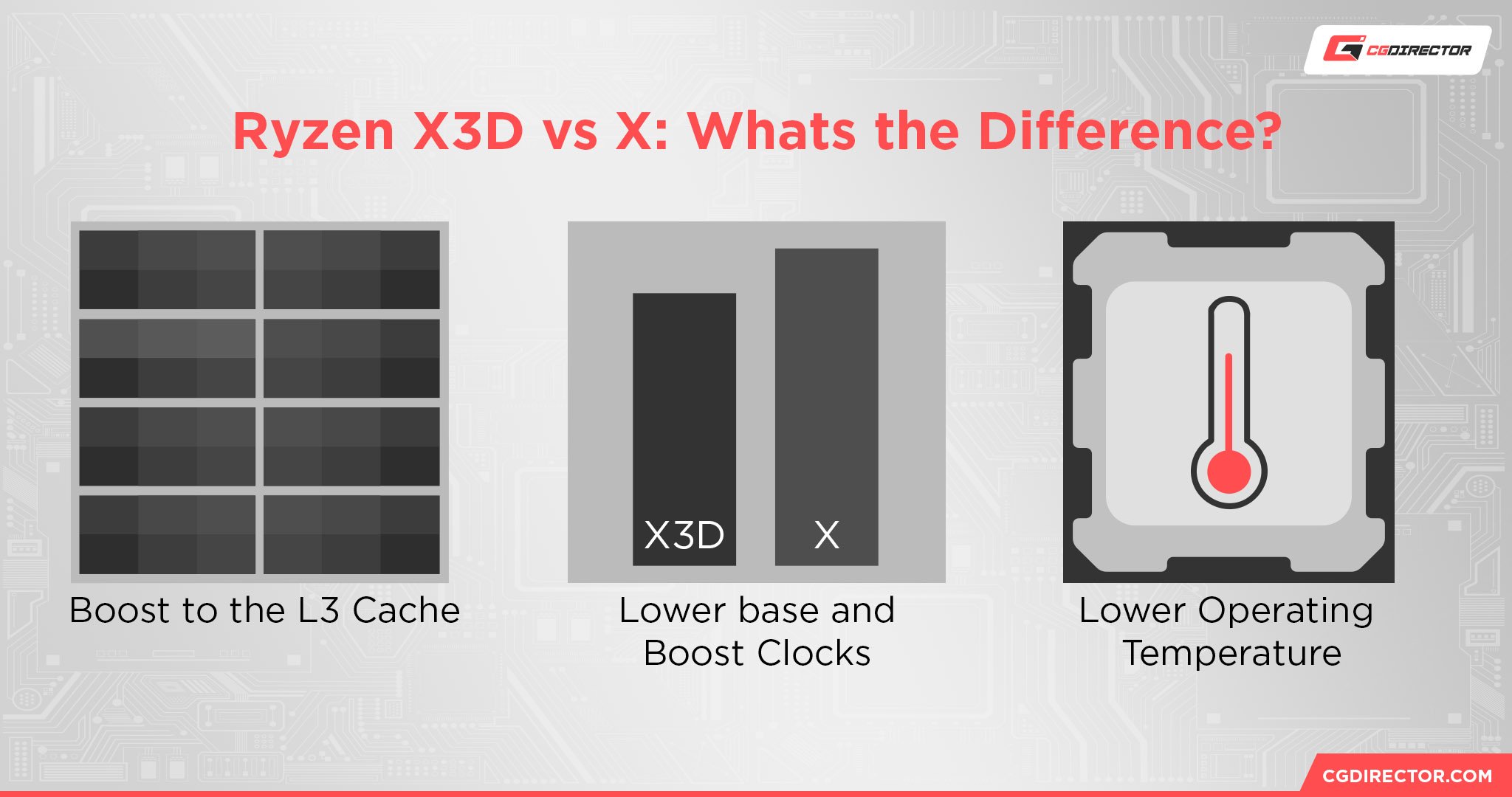
First, let’s talk about the main difference.
AMD Ryzen X3D CPUs are pretty similar to their standard X counterparts.
Based on their tiering, the X3D variants still offer the same core and thread count as the X version of that CPU, or in the case of the Ryzen 7 7800X3D, the same core/thread count as the 7 7700X.
The naming is different on that pair, but they are still mostly the same CPU as with the matching-name pairs of Ryzen X and Ryzen X3D CPUs.
Ryzen X3D CPUs make the following changes to the design:
- A massive boost to L3 Cache. AMD calls it “3D V-Cache” due to the manufacturing method actually requiring 3D “stacking” of the L3 Cache onto the main processor cores.
- A downward adjustment to Base and Boost clock speeds. This is usually a few hundred Megahertz.
- A lower peak operating temperature. Because 3D V-Cache requires stacking CPU cache memory directly on top of CPU cores, X3D CPUs are much more sensitive to overheating and require more safeguards. More on those soon!
Now, how do these changes impact your out-of-the-box CPU performance? Let’s sink our teeth in and start the proper battle between CPUs!
AMD Ryzen X3D vs X: Which Is Best For Your Needs?
AMD Ryzen X3D vs X: General Performance
First, let’s start with the obvious question: do Ryzen X3D CPUs have any obvious differences from their X CPU counterparts in general desktop use? For the end user, I would say no.
The Megahertz adjustment on the cores impacts performance in some areas, but these differences should be pretty much undetectable for general desktop use like web browsing or media consumption.
All your cores and threads will still work fine on the X3D version of the CPU, and at the Ryzen 7/Ryzen 9 points where these CPUs currently start being sold, you’re already well beyond the necessary CPU budget for a smooth, seamless desktop use experience.
To properly appreciate the difference these CPUs actually have to offer, we’ll need to take a look at heavy-duty workloads.
AMD Ryzen X3D vs X: Rendering and Productivity Performance
AMD Ryzen CPUs have always been fairly popular for rendering and productivity performance. AMD CPUs have generally focused on offering superior multi-core performance for the dollar for a long time now, even before the launch of Ryzen in 2017.
The caveat to this has always been reduced single-core performance when compared to the latest and greatest from Intel, though Ryzen has significantly improved AMD’s per-core performance, enough to reignite competition in the CPU market.
For professional purposes, AMD Ryzen’s marginal disadvantages in per-core performance have typically been easily overshadowed by their great performance-per-dollar.
If you know how to put that raw throughput to use in your workloads and aren’t reliant on any Intel-specific features, Ryzen CPUs are known to be multi-core powerhouses.
So, what about Ryzen X3D CPUs? It turns out this is the key compromise between Ryzen X3D and Ryzen X CPUs.
Multi-core performance actually takes a hit on Ryzen X3D CPUs, and this hit results in an overall performance loss for rendering and productivity applications reliant upon raw multi-core throughput.
The severity of this performance loss is going to depend on your specific Ryzen X3D CPU. However, the most severe example of this discrepancy is present on the original Ryzen X3D CPU, the Ryzen 7 5800X3D, compared to the Ryzen 7 5800X.
I’ve embedded a screenshot from Puget System’s productivity benchmarking below:
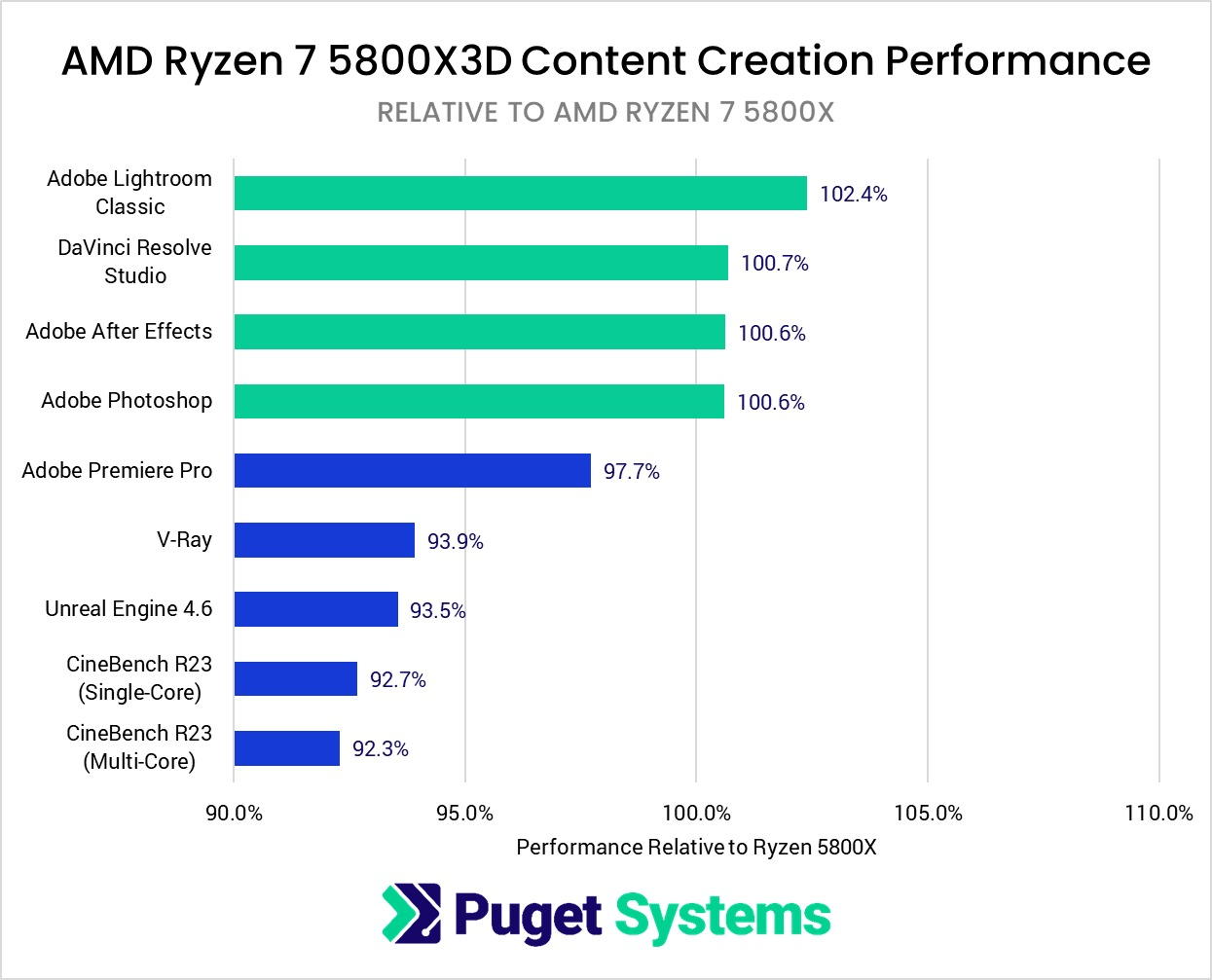
Source: Puget Systems
As you can see, the best-case scenario for the Ryzen 7 5800X3D is photo editing. Once you start putting it through its paces in heavy-duty rendering and code compilation workloads that scale well across many cores, the weaknesses of the 5800X3D begin to show themselves.
When we move onto the 7900X3D and the 7950X3D, most productivity workloads have improved to be more on par with the non-3D CPUs. However, video editing with DaVinci Resolve has taken a considerable dip.
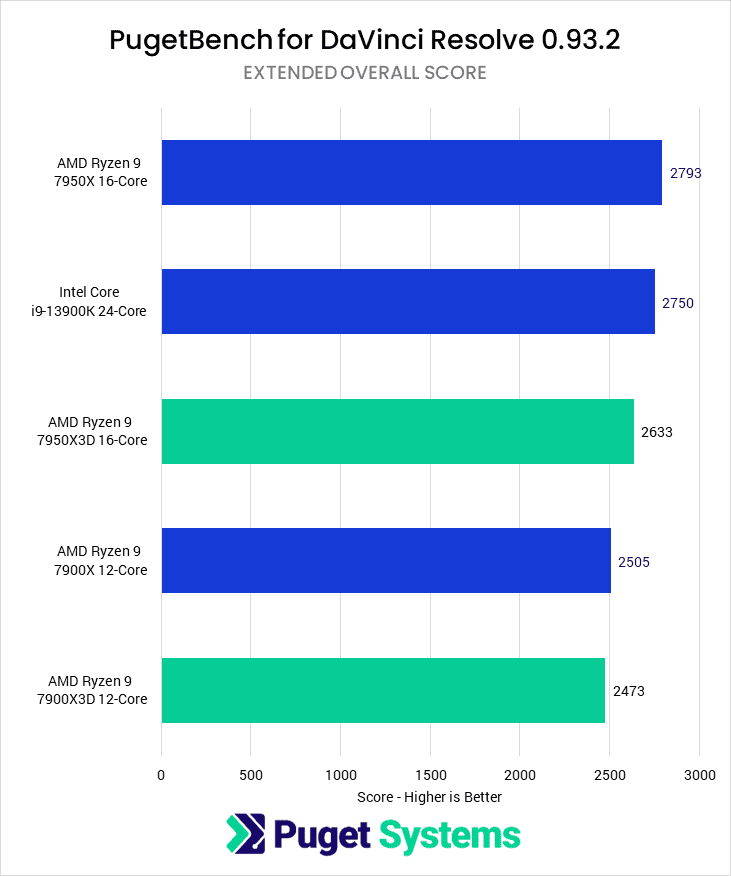
Source: Puget Systems
So even though newer X3D CPUs improve upon the multi-core compromises X3D introduces, the best choice for a professional will nearly always be the Ryzen X CPUs, especially where pricing is concerned.
AMD Ryzen X3D vs X: Gaming Performance
This is arguably the comparison point that matters the most when comparing Ryzen X3D and Ryzen X CPUs.
It’s no accident, either: Ryzen X3D CPUs are tailored for gaming specifically, with the huge boost in L3 Cache targeted at improving the per-core performance of X3D CPUs.
The workload most impacted by single-core performance is PC gaming, and this has corresponded to a general lead in gaming performance by Intel throughout the years, even though Ryzen X CPUs have become more competitive on that front.
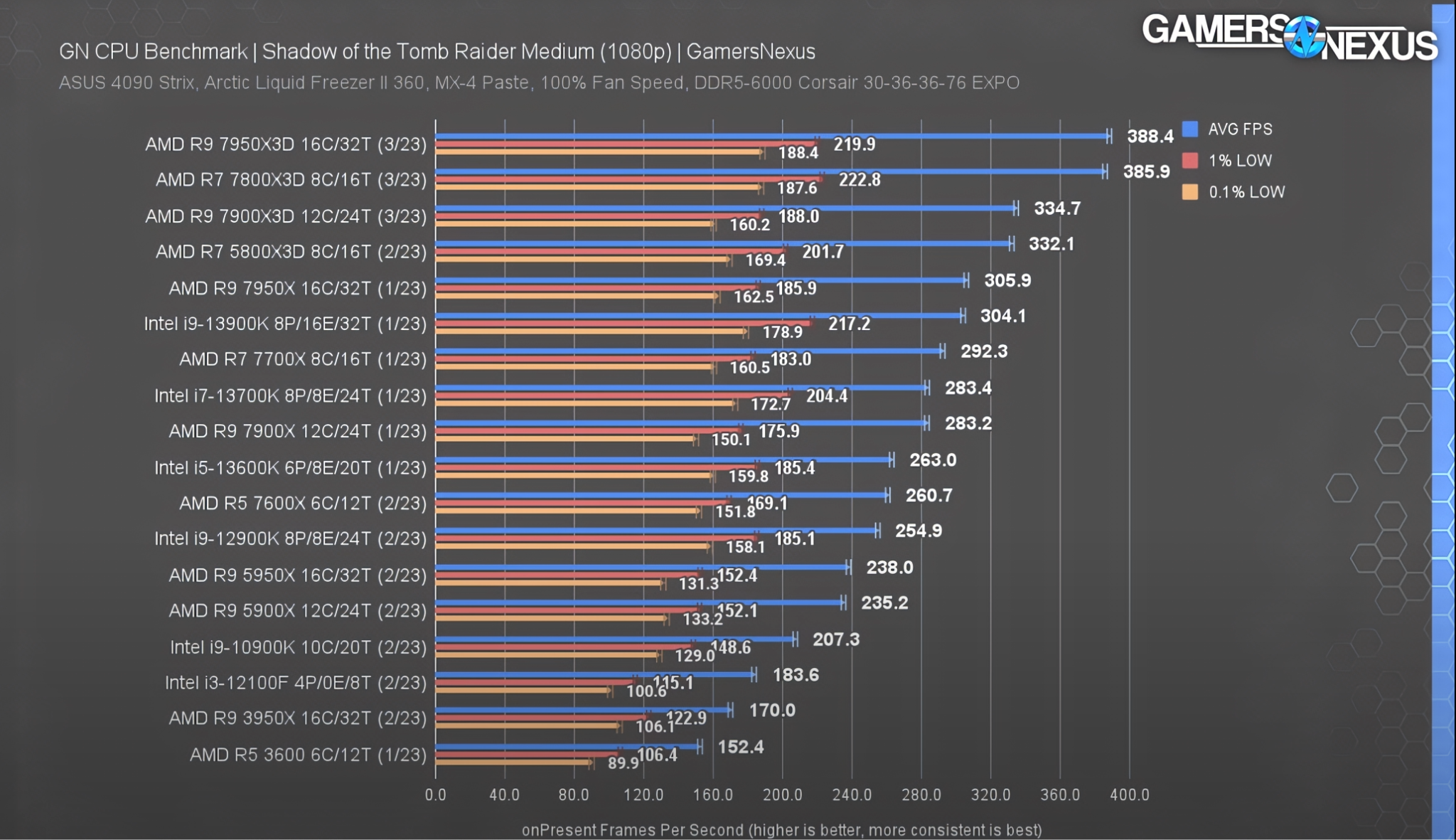
Source: GamersNexus
So, how big is the difference when you start pulling out the gaming benchmarks?
Well, it can vary a bit depending on the game, but overall, Ryzen X3D CPUs almost always show a fairly strong boost in gaming performance when compared to their non-3D counterparts.
With some titles, this can be 5% or less, but with most, it manifests as a 10-20% gaming performance delta between Ryzen X and Ryzen X3D.
That’s not bad at all, and it’s been giving AMD a strong leg up over Intel in the gaming CPU market— and that is no small feat.
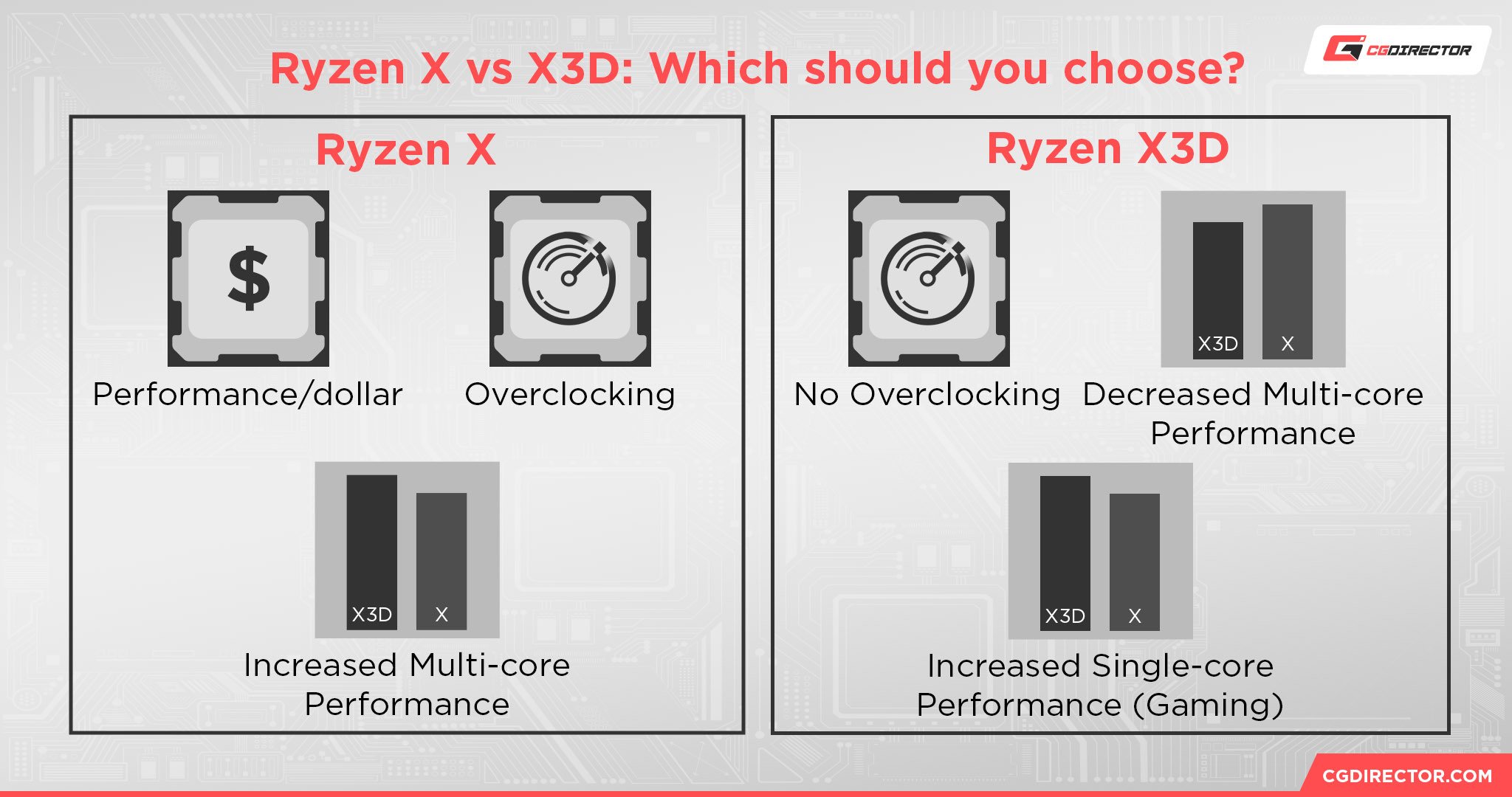
AMD Ryzen X3D vs X: Choosing The Best One For You
And now, it’s time to start wrapping up this direct comparison!
Which is better for you: AMD Ryzen X CPUs, or AMD Ryzen X3D CPUs? At the end of the day, these CPUs perform nearly the same in most workloads, especially if you opt for a newer-gen X3D chip that does more to mitigate the multi-core downsides of the altered architecture.
However, even the best-case scenario for Ryzen X3D in productivity workloads is a bit overshadowed by the price difference, which is often $100 or more just for 3D V-Cache on the CPU.
So, overall, I would break it down like this.
Go with Ryzen X CPUs if:
- You want to maximize your CPU performance-per-dollar.
- You don’t need cutting-edge gaming performance.
- You’ll be making good use of the better or at least as-good multi-threaded performance at a lower price point.
Go With Ryzen X3D CPUs if:
- You want cutting-edge gaming performance.
- You’re able to accept some compromises to multi-core CPU performance.
- You can afford to pay for the price hike between Ryzen X and Ryzen X3D CPUs.
FAQ
Does Ryzen X3D Support Overclocking?
For the most part, no.
Ryzen X3D CPUs have stricter clock speed limits and even a lower maximum operating temperature than their X CPU counterparts, which makes them a suboptimal choice for overclocking.
Plus, AMD disables overclocking* on Ryzen X3D CPUs, though Precision Boost Overdrive and other workarounds are still available for you to use at your own risk.
*Since AMD goes out of its way to disable overclocking on Ryzen X3D, circumventing it means voiding your warranty. Ouch!
Understandable, though: remember, that “3D” means that your L3 Cache is being stacked on top of your CPU cores, which means the thermals must be more tightly-controlled to protect system stability.
This also corresponds to better cooling and performance-per-watt on the X3D CPUs, though you’ll still want a powerful CPU cooler due to the lower maximum operating temperature (90 degrees compared to the standard 95 degrees.)
Are Ryzen X3D CPUs More Likely To Overheat and Fail?
No, however, if you have a Ryzen X3D CPU you should probably make sure that you keep your BIOS up to date.
Ryzen X3D CPUs are actually more vulnerable to voltage issues than pure thermal issues, but voltage problems for the launch of the 7800X3D actually were bricking some systems with memory overclocking applied due to manufacturers going outside AMD’s intended spec.
This was fixed with BIOS updates but was still a real problem for a while there.
Are Ryzen X3D CPUs Better Than Intel For Gaming?
Well…yeah, at least for now!
Intel CPUs may have held the gaming performance crown for a long time, but as of the time of writing, the Ryzen 7 7800X3D is considered the best gaming CPU on the market, with performance outstripping that of even its own 3D V-Cache Ryzen 9 sibling.
I expect the next Intel refresh will force some power out of AMD’s hands, but overall I’d say boosting L3 Cache has proven to be one of AMD’s best moves for improving their CPU’s gaming performance in a long time.
Over to You
And that’s it! I hope this article helped you determine the winner of AMD Ryzen X3D vs X CPUs for your next PC build.
Feel free to let us know in the comments below which one you’re going for, or if you have any additional questions about Ryzen CPUs or PC hardware in general.
Alternatively, you can also head over to the CGDirector Forums for more in-depth discussions with the rest of the team and community of experts and enthusiasts! We’ll be happy to have you.
Until then or until next time, happy computing! And if you’re going with an X3D processor…happy gaming. Better stay off 32-man KOTH_Harvest, though. That’s my kingdom.
![Best CPU for Video Encoding [2024 Update] Best CPU for Video Encoding [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2022/02/Best-CPU-For-Video-Encoding-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![Is AMD’s AM5 Socket Backwards Compatible? [Quick & Easy] Is AMD’s AM5 Socket Backwards Compatible? [Quick & Easy]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/01/Is-AMDs-AM5-Socket-Backwards-Compatible-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![AMD Ryzen 5 vs Intel Core i5: Full Comparison [2024 Update] AMD Ryzen 5 vs Intel Core i5: Full Comparison [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/10/Ryzen-5-vs-Core-i5-Full-Comparison-With-Pros-and-Cons-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

0 Comments