TABLE OF CONTENTS
PCIe Riser and Extension Cables have become more and more important in recent years.
Ever since manufacturers started designing innovative PC cases, placing GPUs vertically, or workstation users and miners needing more GPUs than easily fit inside standard cases, riser cables have become an integral part for many PC-Builders.
Mini ITX and Micro ATX cases are becoming more common and GPUs are often position further away or at an angle of their corresponding PCIe-Slots on the Motherboard.
Why Use a PCIe Riser?
There are two main reasons why you might want to use PCIe Riser cables:
- Space constraints: Better / Possible GPU placement for Single- or Multi-GPU Configurations & possibly better cooling. Especially for low-profile GPUs in Small Form Factor Cases that would otherwise clash with low-profile CPU Coolers.
- Aesthetic Reasons: Showing off your GPU in other orientations
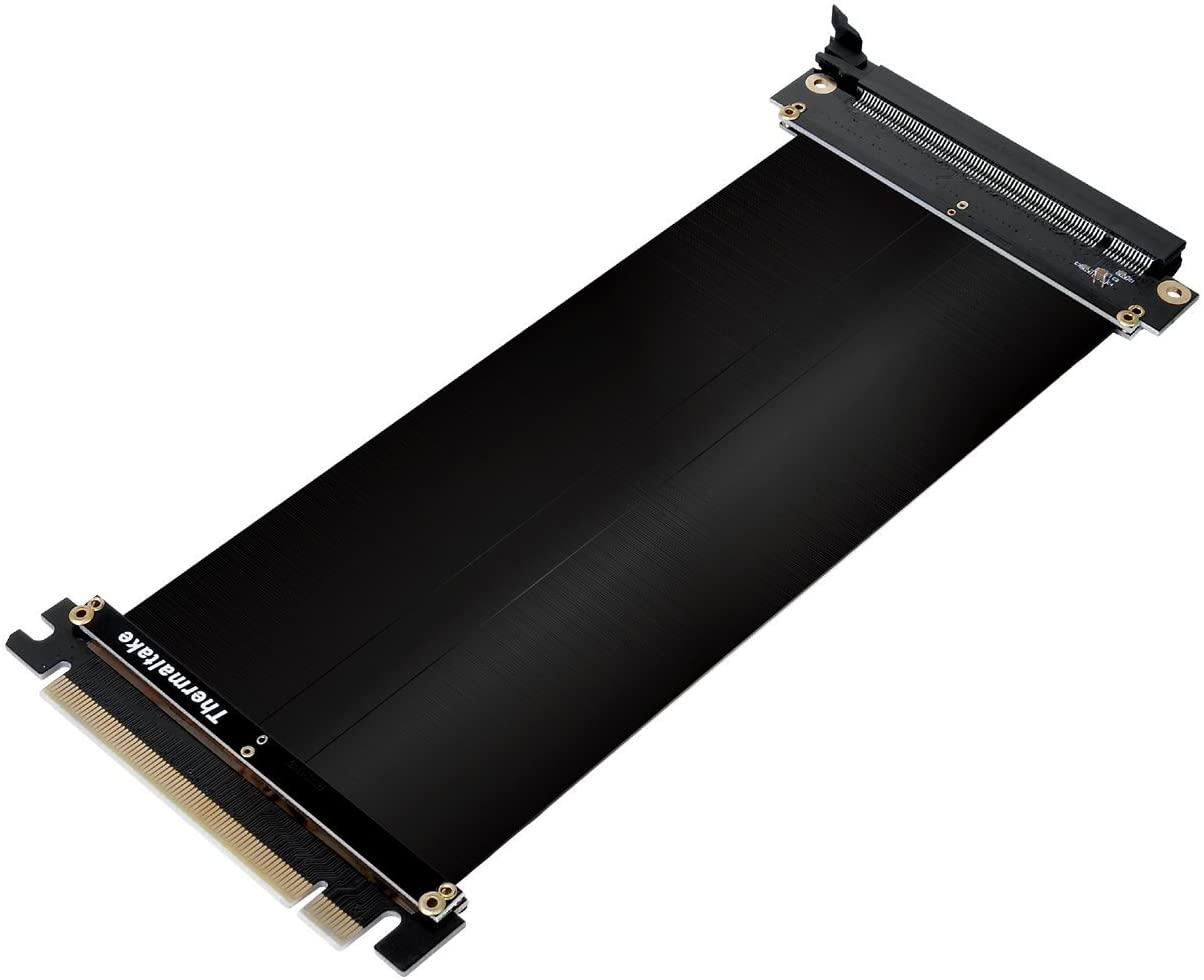

Image-Credit: Thermaltake
There is one Component that has not kept up with the minification of many PC-Parts: the Graphics Card.
By their nature, GPUs are still fairly large and bulky. They have built-in fans that require a certain amount of space.
And while smaller circuitry has become more efficient, the growing demands on a modern GPU have meant that each generation, manufacturers concentrate on making their GPUs more powerful at the same dimensions, rather than developing smaller GPUs.
The reason for this is obvious.
For gamers, content creators, and cryptocurrency miners, the GPU is a crucial aspect of their system. If you’re forced to choose between a faster GPU at the same size or a smaller GPU with less performance, faster wins in most cases.
If you’re building your own PC or upgrading an older system, this can be a major inconvenience.
Getting the right placement for your case fans, in particular, can be a difficult task.
This is especially true if you want to overclock your GPU and other components.
Sometimes, it’s easier to relocate your GPU than relocate a fan. This is where a PCIe riser or extension cable comes in. Essentially, they allow you to move the GPU to a different location inside your case or use an open mining case.
You can put your GPU closer to your water block if you have a liquid-cooled PC, or up against the case’s window for maximum visual impact.
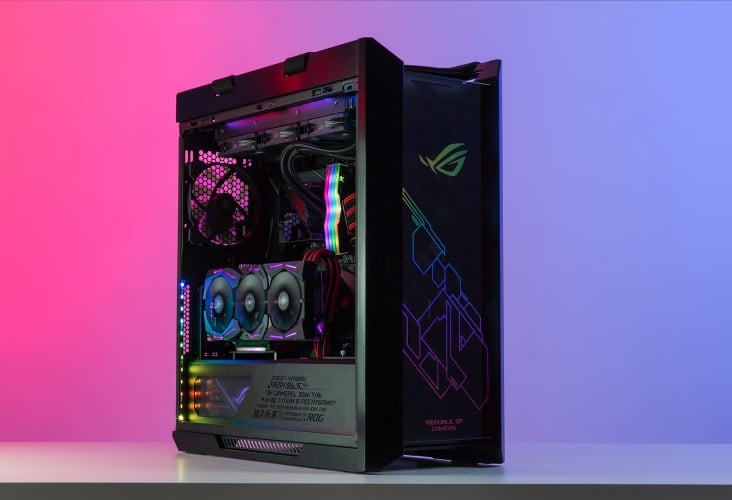

Image-Source: Asus
This is especially true for multi-GPU systems. If your motherboard will support it, running multiple GPUs will dramatically improve the performance of many workloads such as GPU Rendering.
For Multi-GPU configs, the spacing of the PCIe-slots on the motherboard will often be sub-optimal to mount all of your GPUs directly.
But a graphics card is only as good as its connection to the motherboard, so let’s find the best PCIe risers and extension cables to meet your needs.
What’s the Difference Between Different PCIe Standards?
PCIe slots come in different types, electric bandwidths, and mechanical sizes (length). The longer the slot, the higher the bandwidth supported.
GPUs have high bandwidth needs and usually require the longest type of PCIe-slot, namely x16 PCIe-slots.
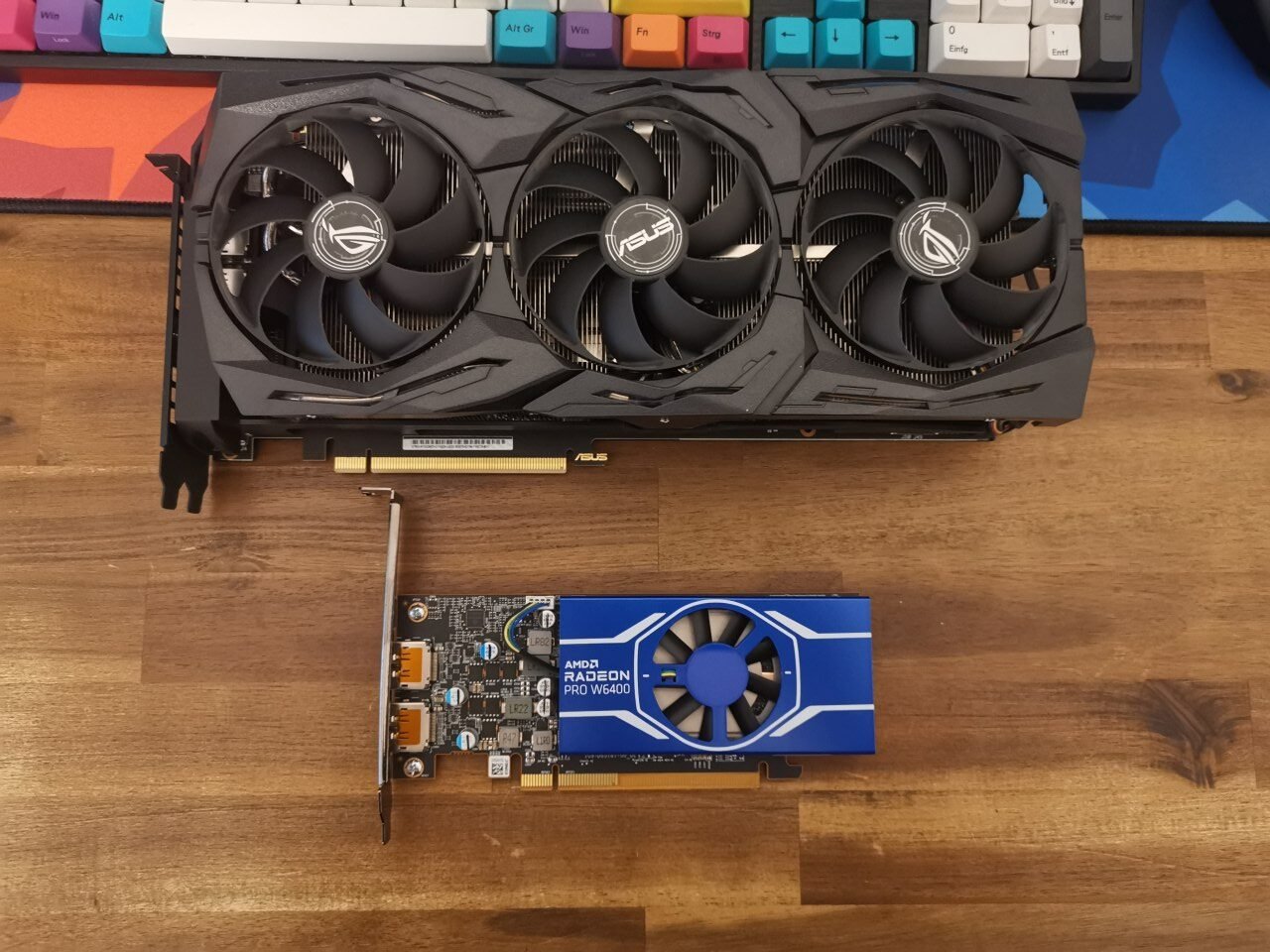

The AMD Radeon Pro W6400 is extremely small compared to a 2080 Ti
The yellow pins at the bottom of this GPU plug into the PCIe-slot of a motherboard.
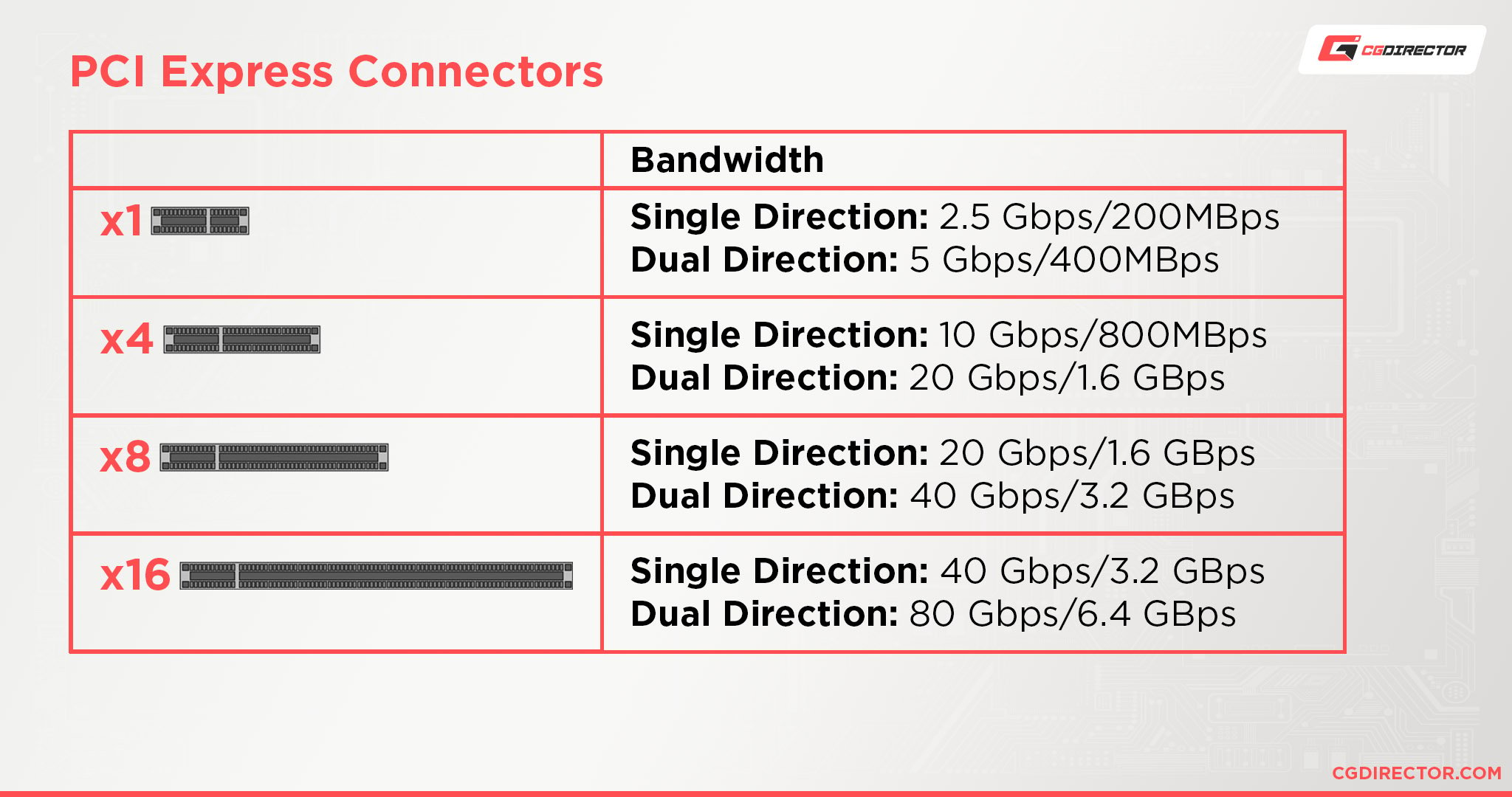
Now, x16 is not a fixed bandwidth but depends on the generation of the PCIe interface we are talking about.
As you can see in this table, x16 on a PCIe 2.0 Generation is half as fast as x16 on PCIe 3.0.
| PCIe Bandwith | Bandwidth x1 (per lane) | x4 | x8 | x16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCIe 1.0 | 250 MB/s | 1.00 GB/s | 2.00 GB/s | 4.00 GB/s |
| PCIe 2.0 | 500 MB/s | 2.00 GB/s | 4.00 GB/s | 8.00 GB/s |
| PCIe 3.0 | 984.6 MB/s | 3.94 GB/s | 7.88 GB/s | 15.75 GB/s |
| PCIe 4.0 | 1969 MB/s | 7.88 GB/s | 15.75 GB/s | 31.51 GB/s |
Nvidia’s RTX 10xx and 20xx generation GPUs for example run on PCIe 3.0 and require a “mechanical” x16 pcie-slot.
Why mechanical? Because you can differentiate between a x16 slot which is mechanically long enough to fit x16 GPUs but might “electrically” be slower and only transfer Data at x8, or even just x4 speeds.
If you’d like to learn more about this, do check out our GPU articles here and here.
So, long story short, for PCIe-Riser cables, you’ll have to know a couple of things before you can start shopping for one:
- Know the required electrical bandwidth of your GPU(s) (e.g. x16 PCIe 3.0)
- Know the required mechanical slot type required by your GPU(s) (usually x16 too)
There are cases when GPUs, although they are both x16 mechanically and electrically, aren’t fast enough to saturate the Bandwidth of a x16 PCIe-slot.
Anything inferior (performance-wise) to an Nvidia 2080 Ti, for example, will perform the same on both an electrically x8 or x16 PCIe-Slot. This is because the GPU’s Bandwidth is not high enough to saturate (be faster than) the bandwidth of an electrical x8 PCIe-Slot.
We’ve written an extensive Guide on PCIe Lanes for additional info.
What Should I Look For in a PCIe Riser?
So, what should you look for in the best PCIe Riser Cable? There are a few different factors you should look for.
There are two main types of PCIe riser cables: powered and unpowered.
Powered riser cables utilize a secondary power supply. This is usually an internal USB connection, but it can also be SATA or even a MOLEX port. Generally, powered risers connect to an x1 or x4 PCIe port and have an x16 adapter for the GPU. As a result, they’re usually used by crypto miners.
The reason is simple: Although the GPU-facing Slot has a mechanical x16 Interface, the Motherboard facing connector only is x4 and therefore can’t transfer at higher speeds than x4 Bandwidths.
This is only right for you if you know you won’t need higher Bandwidths than x4. Usually, just miners or very un-demanding workloads can get away with this.
If you’re buying a powered riser, it’s a good idea to look for USB 3.0 support. This makes it easier to connect to your motherboard. In addition, look for the number of capacitors. The more capacitors, the more stable the power supply. Look for a riser with at least three capacitors to get the best performance.
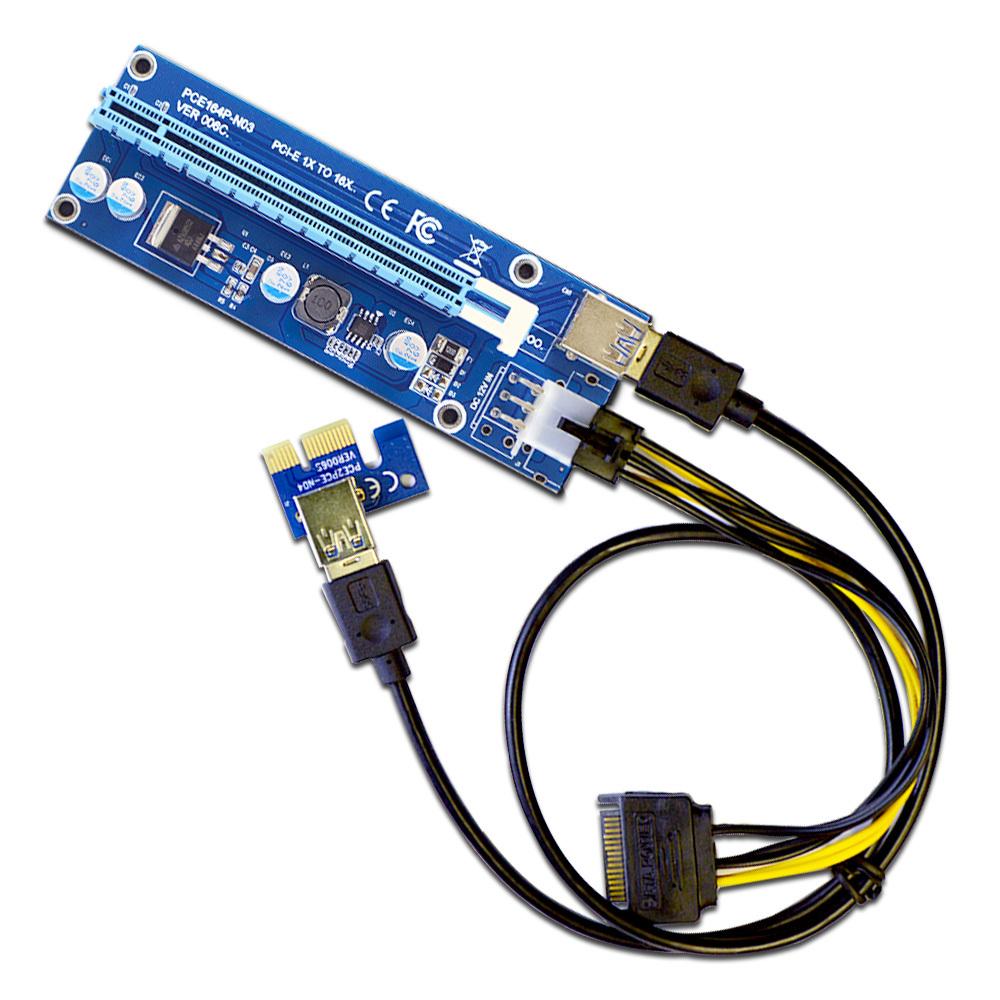

Un-powered risers, as the term implies, do not draw power from an external source. These risers draw power directly from the motherboard’s native x16 PCIe port. Typically, these risers function like simple extension cables.
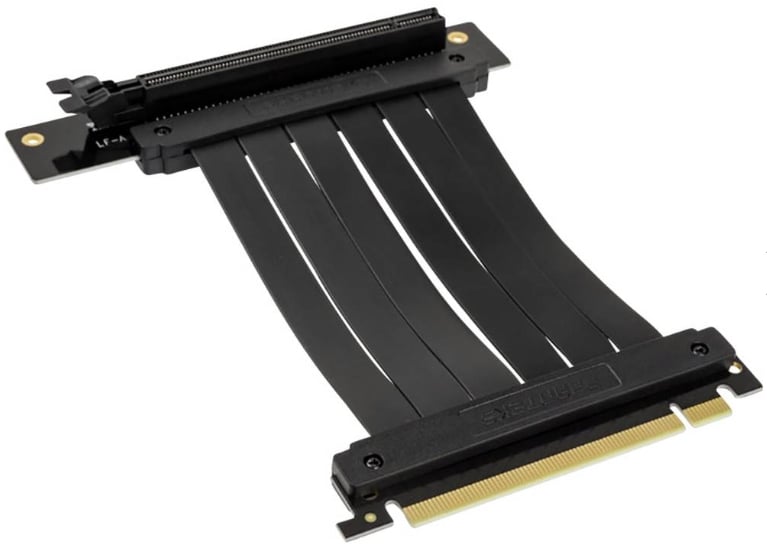

Image-Credit: Phanteks
I’ve Heard of M.2 Adapters – Are They Any Good?
If you’ve been shopping around for a PCIe riser, you may have heard of an M.2 adapter. Typically, an M.2 adapter is used for internal accessories such as an SSD. But you can also use them for lower-tier graphics cards if you use an M.2 adapter.
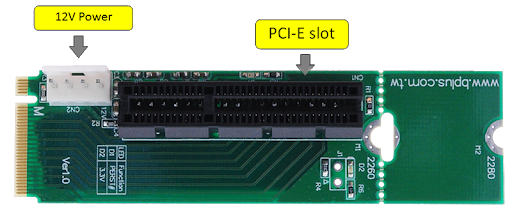
Installing an M.2 adapter is generally very easy. You simply plug them into your M.2 slot, screw them down, and connect the SATA cable. It doesn’t get much easier than that.
Unfortunately, M.2 adapters are not suitable for content creation or gaming. The reason is that the M.2 slot has a data transfer rate equivalent to an x4 PCIe slot. This is just fine for crypto mining, but it’s not good enough for more demanding workloads.
Are Mining Motherboards Any Good for Content Creation or Gaming Workloads?
With the growth in popularity of crypto mining, some manufacturers have started releasing motherboards with a large array of PCIe ports. For example, check out this ASUS motherboard, with a single x16 slot, and a whopping 18 x1 slots for connecting a large GPU array.
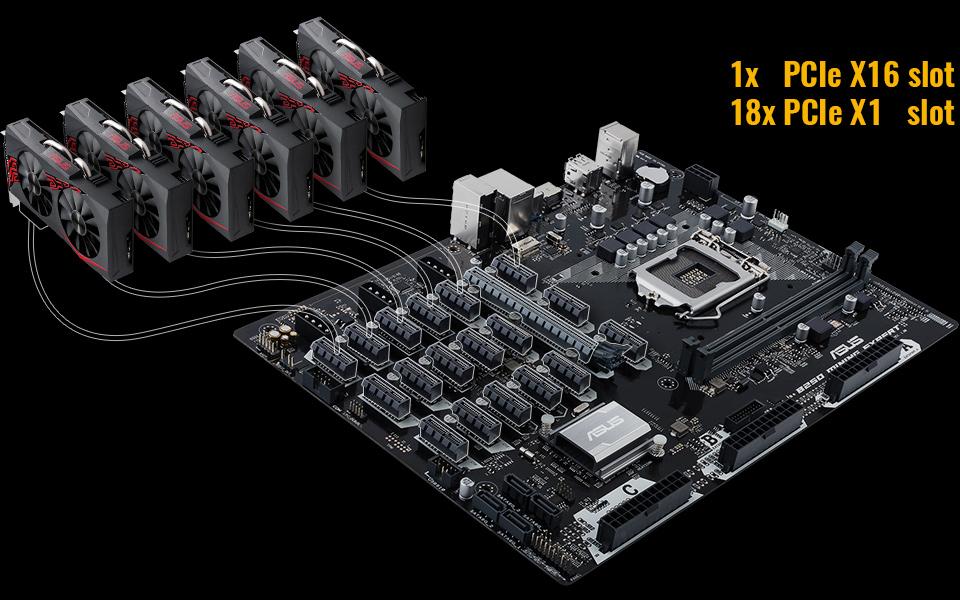

Image-Credit: Asus
Obviously, these x1 PCIe-Slots are a terrible choice for content creation or gaming as you’ll need much higher bandwidths for decent performance.
Of course, if you do both, Mining and Gaming, for example, having a Motherboard with a single x16 slot with a GPU in it for Gaming, and a bunch of Mining GPUs attached to the x1 Slots would be a possibility.
What Are PCIe Extension Cables?
An extension cable is just another type of PCIe Riser Cable. Instead of a bracket, they’re just a simple male-to-female PCIe cable.
Extension cables are designed to allow for more flexible placement of your GPU. They’re ideal for maximizing your cooling system’s performance. If you’re a content creator or gamer, this is the type of “riser” you want to invest in.
For example, suppose you’re building a multi-GPU system for GPU rendering. By spacing the GPUs further apart from each other you would be able to keep the Temperatures lower, enabling longer boost and higher clocks on your GPUs – resulting in shorter render times. Or higher FPS in Games.
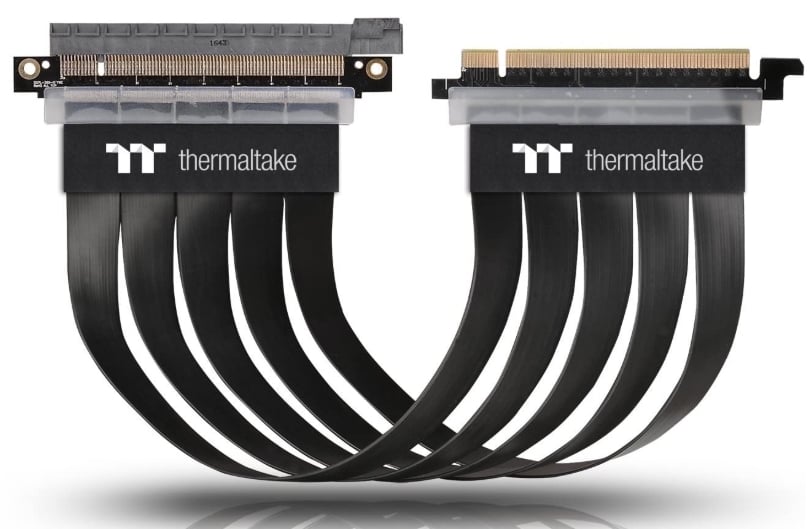

Image-Credit: Thermaltake
When you’re buying an extension cable, longer isn’t always better.
To be fair, a longer cable gives you more options for GPU placement. On the other hand, it presents some challenges for cable management. A shorter cable, on the other hand, requires less cable management.
Longer cables can also decrease the quality of the signal that is transferred (Impedance), so be sure to get as short a cable as possible, especially when you are in need of high bandwidths.
Will a PCIe Riser Cable Affect My Performance?
Provided you use a quality riser cable and handle it carefully, it will not affect your performance negatively. That said, there are a few caveats to that.
- If you’re daisy-chaining PCIe cables, you may run into some power supply issues. This will depend on how well-engineered the cables are. For gaming or content creation, this won’t be an issue, since everything is presumably inside the case. But if you’re putting together a GPU array for crypto mining, check the manufacturer’s ratings for daisy-chaining.
- Another potential issue is the quality of the locking mechanism. Make sure the lock is nice and sturdy and keeps the plug securely in place. If the lock is flimsy, you might end up breaking it during installation. This can really ruin your day.
- Finally, a good magnetic shield can be a great help. If the cables are shielded with TPE, this will go a long way towards reducing interference from any nearby sources of interference.

Best PCIe Riser Cables / Extension Cables Recommendations
We’ve talked about all the basics. Now, it’s time to take a closer look at our top picks.
Highest Quality PCIe-Riser Cable – Thermaltake AC-045-CN1OTN-C1

Image-Credit: Thermaltake
One way to find the best PCIe riser is to go with a manufacturer you know and trust. For fans of high-end PCs, Thermaltake should be a familiar name. They’re primarily known for their top-notch cooling systems and RGB lighting rigs. But they also make some excellent riser cables.
The Thermaltake AC-045-CN1OTN-C1 is a PCI-E x16 3.0 Riser Cable that will enable the full Bandwidth for your PCIe-3.0 GPUs.
The riser cable measures 30cm in length, making it a great choice for long runs. The riser cable is housed in five separate ribbons, which allows for better shielding than a single ribbon.
Each ribbon is encased in a layer of TPE plastic shielding, with additional PE insulation on the individual copper wires. This allows for full use of the PCIe-3.0 Bandwidth, with virtually zero interference.
In addition to being well-insulated, the Thermaltake ribbons are also very flexible. Because they’re separate from each other, they can make multiple bends and twists. Even if your PC case is very crowded, cable management is going to be a non-issue.
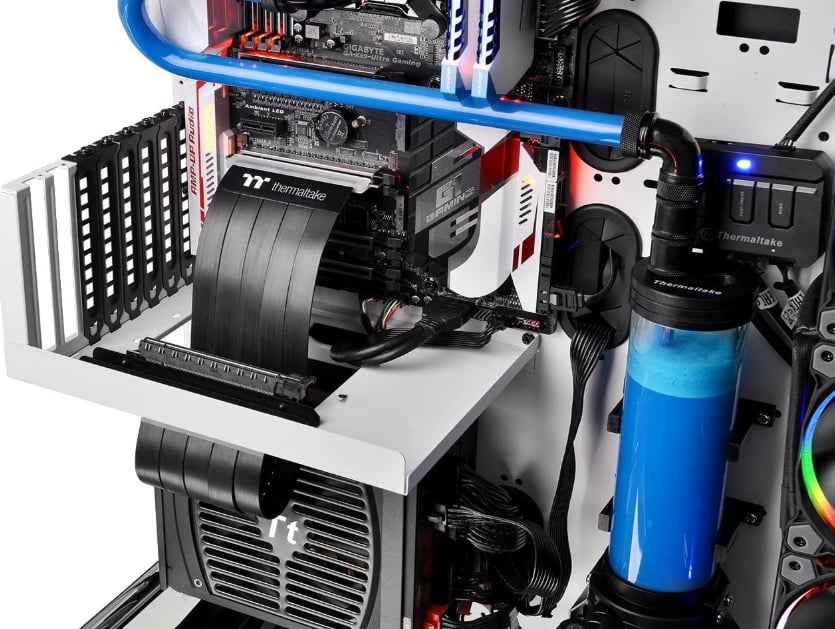

Image-Credit: Thermaltake
Both the male and female connections on the Thermaltake are gold-plated, ensuring excellent conductivity. And the PCBs are beefy and robust.
The clip on the female end is nice and fat, which makes it easy to snap shut for a secure, stable connection
All of this is guaranteed by Thermaltake’s one-year manufacturer’s warranty. Thermaltake is well-known for excellent customer service, so you’ll have no issues there. This cable may be on the expensive side, but it’s by far the best PCIe riser cable on the market.
Runner-Up: Phanteks Premium Shield Riser Cable
As an alternative to the Thermaltake Riser Cable, our runner-up is the Phanteks 600mm Premium Shielded PCIe Riser Cable which has a similar 90-degree tip. However, it’s a full 60cm in length, perfect for very long runs. To ensure signal integrity at this length, it sports shielded twin-axial wires, along with dedicated power lines.
Alternative: LINKUP Shielded Twin-axial Riser Cable
That said, a 90-degree tip can sometimes make cable management easier. In that case, the LINKUP Shielded Twin-axial Riser Cable is an excellent choice. And with hand-soldered gold plated contacts and five shielded ribbons, you’ll get a fast, clear signal.
For those of you sporting a PCIe-4,0 GPU like the newer AMD Radeon RX5700XT, LINKUP has updated their cables to support full PCIe-4.0 x16 Bandwidth with their newest models.
That’s about it from my side! Let me know your questions in the forum or in the comments! 🙂


![Is PCI Express (PCIe) Backward Compatible? Concerns Explained [2024 Update] Is PCI Express (PCIe) Backward Compatible? Concerns Explained [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/06/Is-PCIe-Backward-Compatible-Concerns-Explained-Twitter-594x335.jpg)


8 Comments
15 June, 2022
Are you aware of any powered risers that are at least PCIe 3.0 x8? I want to use an ASUS Sage MB with 7 x RTX 3090’s for rendering, but need a way to separate the power to the cards from the power to the MB. I could use the mining type risers, as Puget Systems did some testing with lane scaling and a 2080 Ti and only found a 7% difference between pcie2x1 and pciex16 rendering with OctaneBench. But with the amount of $ put into the system why leave 7% on the table.
19 June, 2022
Hey Ian,
Benchmarks aren’t the best performance indicator as they’re using extremely simple scenes. Lower poly models, low-res textures, low-resolution render etc. The PCIe bus isn’t strained in such benchmark renders at all.
Once you do some serious work on more complex scenes where a lot more data has to be uploaded to the GPU over the pcie bus, performance is impacted more strongly by fewer pcie-lanes / gen.
Which ASUS Sage are you looking at? The older x299 or wrx80 for TR pro?
Are you looking to supplement the max 75w from the pcie-slot through a powered riser? Not sure that is possible. The bulk of the power will come through the PSU directly.
Cheers,
Alex
17 January, 2022
Using an unpowered riser, would you simply plug the GPU into the PSU using the VGA cables as you normally would?
19 January, 2022
Hi Dan,
Yes 🙂
Cheers,
Alex
21 July, 2021
Is it possible to customize a pcie riser cable? I mean, for aesthetics purposes.
For example, changing the angles, colors, materials, etc.
21 July, 2021
Hey Alex,
I don’t think there are specific sleeves for riser cables, but you can always get led strips that you run along the cables.
Cheers,
Alex
15 January, 2021
I’d like a round PCIe x16 cable, same as they used to make round IDE cables. Is this possible? If I put the Aorus 3080 GPU in my PCIe slot, it’d block the chipset light 🙁 That’s no good! I know they have external enclosures or stands (vanity stands lol), and they accept PCIe ribbon cables, but the problem is the length and flexibility of these cables. One slight bend and they’re dead… if someone were to make a really good cable that’s round and would allow me to set the vanity riser stand to the side of my case (for show), that’d make mine and many others’ day x) Will 3M step up?
16 January, 2021
Yeah there aren’t any that I know of. You can buy a really long one and try if you can twist them, but the risk of damage is high.