TABLE OF CONTENTS
Bent pins can cause a variety of peculiarities. It could range from not detecting your memory and not booting at all to running just fine.
Why? Because it depends on your luck. If you’ve only messed up a reserved pin that’s set aside for a future processor, you won’t have a problem running your PC now.
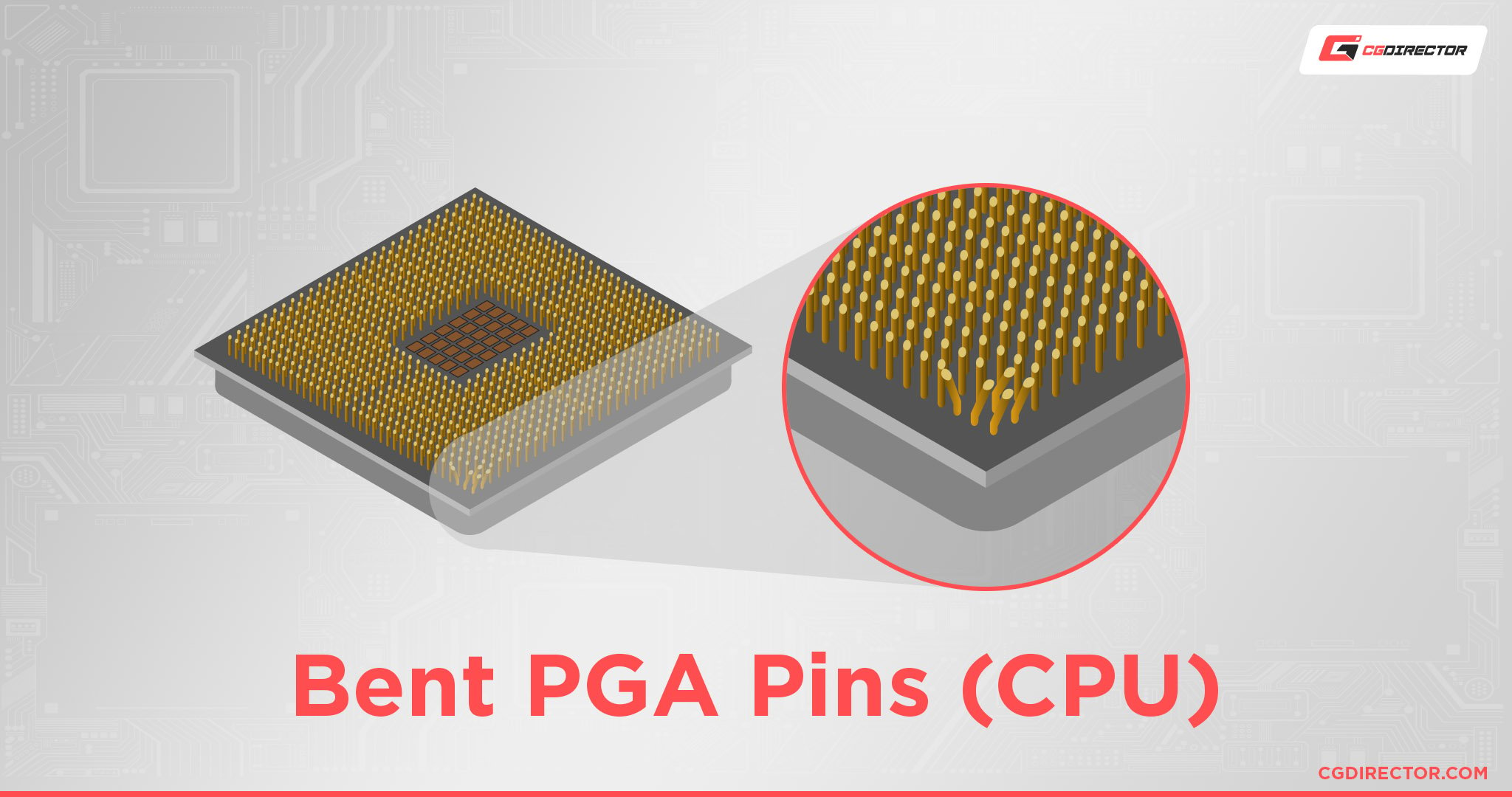
Bent PGA Pins on the CPU
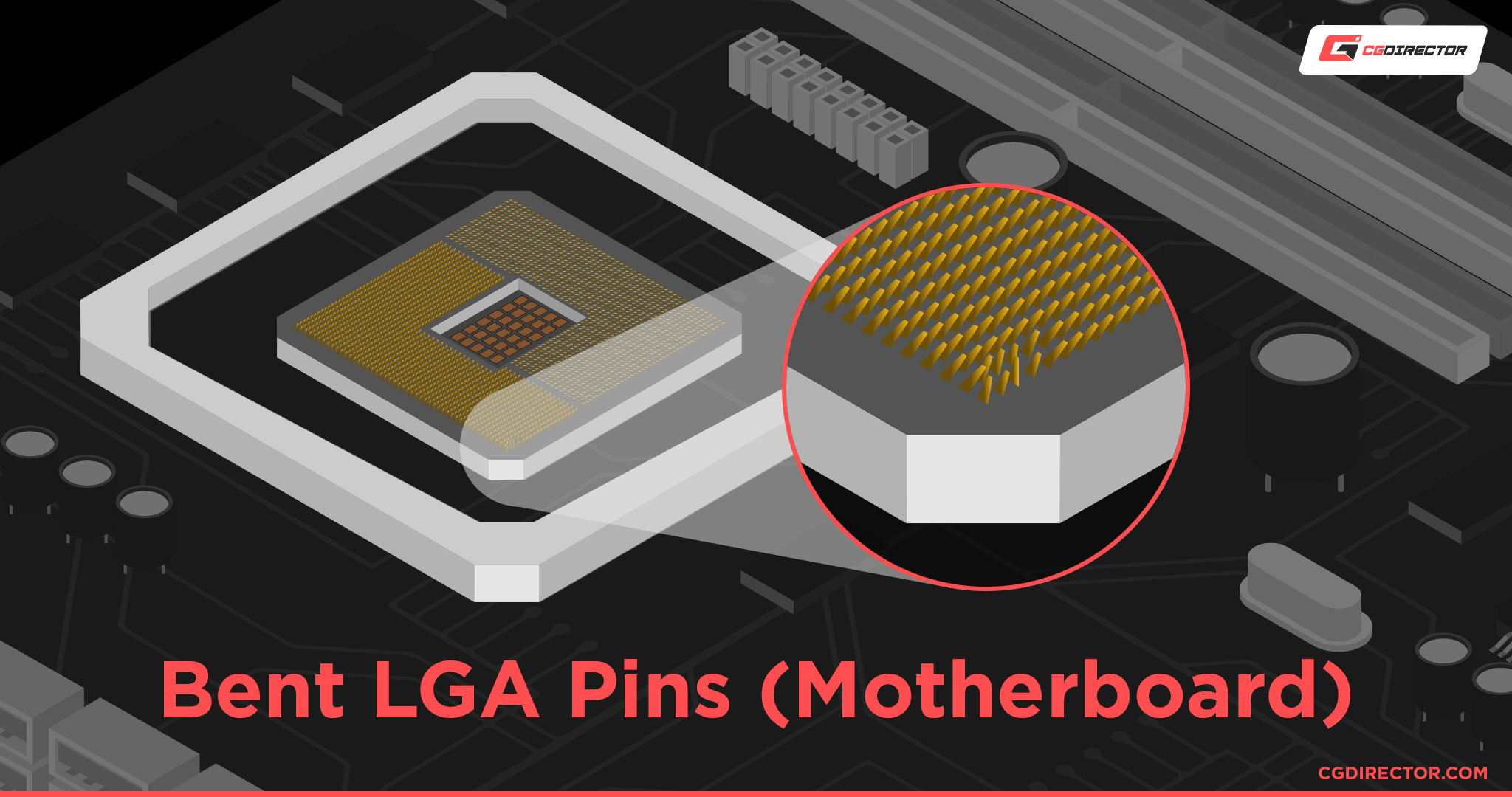
Bent LGA Pins on Motherboard
If you’ve messed up and your poor motherboard socket/CPU looks something like this, well, don’t lose hope yet. There’s an easy fix.
Here’s what to do:
- Check to make sure none of the pins have broken clean off. If they’re all still there, excellent, move on to the next step. If one or more pins have broken clean off, you might have to resort to more risky measures, as shown in this video.
- Check what way the pin is bent. If you’re unsure, look at the socket from as flat an angle as possible.
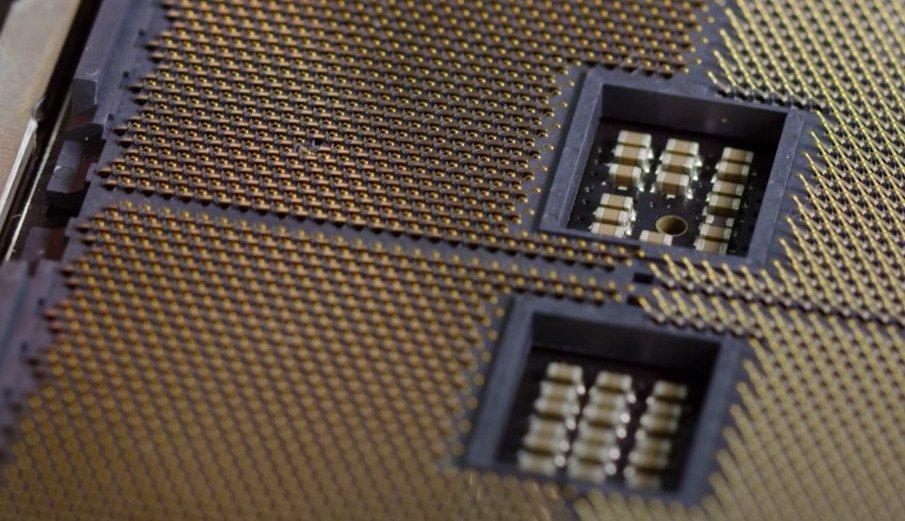
Bent Pins on a TR4 Socket; LinusTechTips
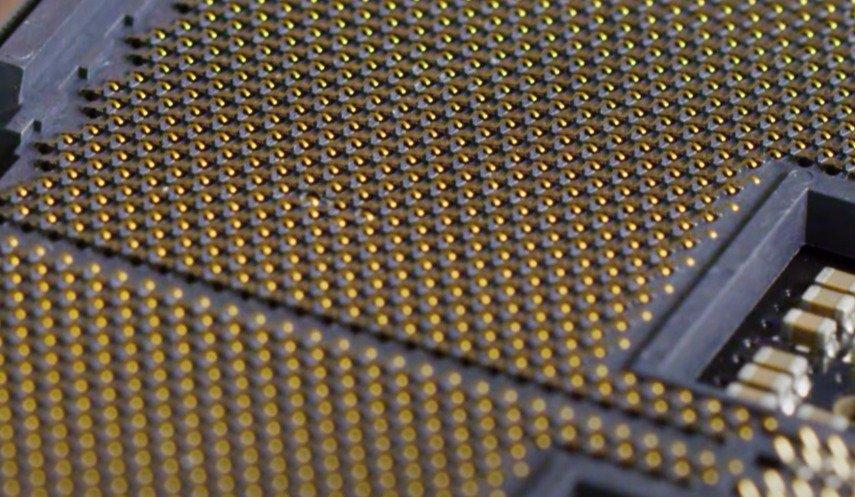
TR4 Socket; LinusTechTips
See the gap in the first image?
A word of warning – if one or more of those pins are severely bent, trying to straighten them might break them. Pins could also snap if you overcorrect and then try bringing them back again. BE GENTLE.
Fixing Bent PGA Pins
Now, there are a few things you can use to straighten PGA pins. A Precision tweezer, the thinnest credit (or any rigid plastic) card you can find, or even a thin-enough screwdriver are viable options. Although many swear by tweezers, I find I’m too clumsy to handle something that requires that much precision. I prefer the card/screwdriver method.
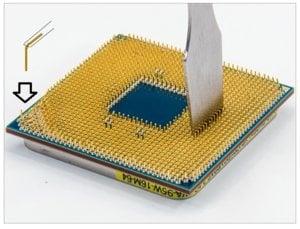
Straightening Bent PGA Pins on AMD Ryzen (Hardware Canucks)
Just stick the screwdriver/knife next to the offending pin(s) and slowly push it(them) back into line. You can see an example of how to go about doing it in the image above.
Fixing Bent LGA Pins
Unfortunately, fixing LGA pins can sometimes be an arduous task. It might require some nifty ‘lifting’ maneuvers.
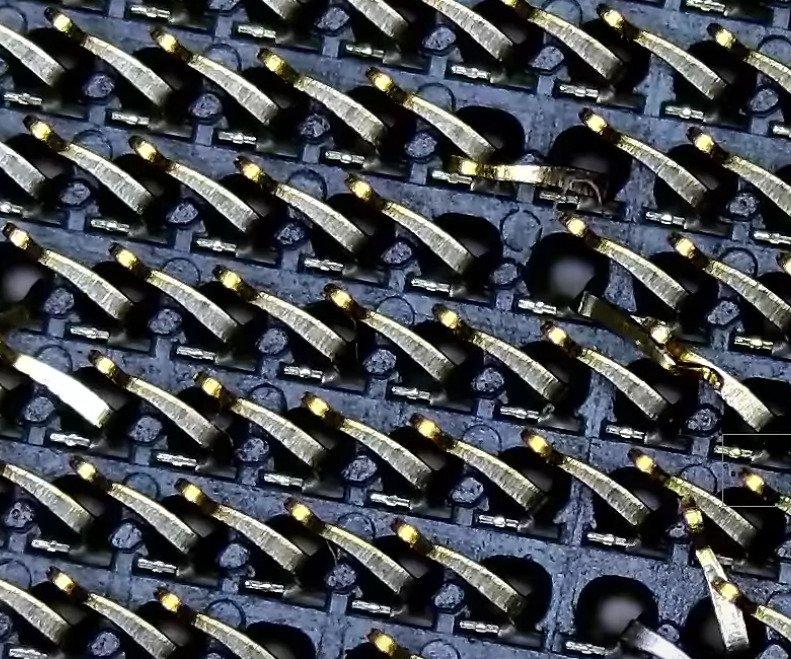

Bent Z390 LGA Pins (Northridge Fix)
In the above image, you can see the pins need to face the correct direction while also matching the other pins’ height. Here’s when a screwdriver or credit card might not be enough. I’d recommend grabbing a pair of tweezers, a sewing needle, or a very thin pocketknife to get those pins straightened out.
Keep in mind, they might not bend back into place perfectly, and your final result could look something like this:
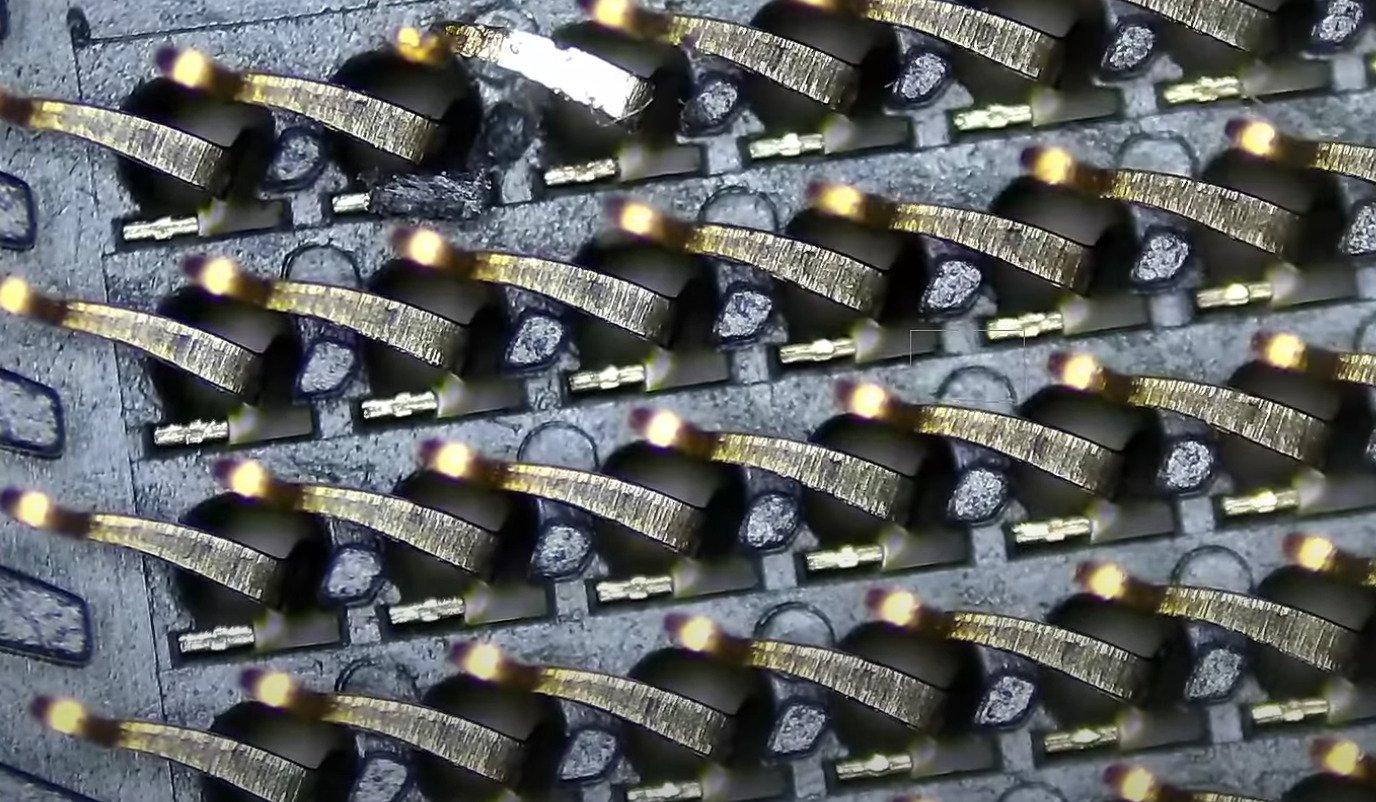

Bent Z390 LGA Pins (Northridge Fix)
Try to get them as close to perfect as possible, and don’t fiddle with them too much because you risk a clean break with every little tug/push.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can You Bend CPU Pins Back?
Yep, sure you can! If the damage isn’t too extreme, this is an easy fix.
What Problems Can Bent CPU Pins Cause?
Well, first – never try installing a CPU when it or the motherboard has bent pins (find more information about LGA vs. PGA here). ALWAYS try to straighten them out as much as humanly possible before using them.
As for the problems they can cause, you can run into a range of issues – from absolutely nothing to a dead CPU if the wrong pin falls off.
What Problems Can Missing CPU Pins Cause?
Unfortunately, there’s no way to know unless you try running it. Some pins are reserved for future processors or might be dedicated to testing. Your processor will run without any issues if one of those pins is missing.
However, if any of the other pins are missing, your issues can range from instability to a dead CPU.
Can You Reattach Broken CPU Pins?
Not really, but if you have managed to break one or more of your pins on a PGA processor, there is a workaround that you can attempt if you’re desperate (assuming you still have the broken pin).
First, identify the pin that fell off from the CPU. Once you see it, look for its matching location on the motherboard’s socket.
Now, slide the broken pin into the correct space on your motherboard socket. Repeat with as many broken pins as you have. Finally, install your CPU by dropping it into the socket very carefully. Here’s a video that shows you how to do it.
Please note that if you do mess up trying this, you are likely to cause further damage to your CPU or damage your motherboard (or both).
Over to you
Have any unanswered questions? Let us know in the comments or our forum!


![What Does The White Light (LED) on My Motherboard Mean? [Updated] What Does The White Light (LED) on My Motherboard Mean? [Updated]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/12/What-Does-The-White-Light-on-My-Motherboard-Mean-Twitter-copy-594x335.jpg)
![How To Fix The Red DRAM Light On Your Motherboard [2024 Update] How To Fix The Red DRAM Light On Your Motherboard [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/11/How-To-Fix-Red-DRAM-Light-on-Motherboard-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

0 Comments