If you’ve ever shopped for processors and motherboards, you would’ve encountered words and terms like ‘sockets,’ ‘LGA1200,’ and so on. In this article, we’ll demystify them for you.
Note – If you’re here wondering if you can fix bent CPU pins, head to the linked article for instructions and more information.
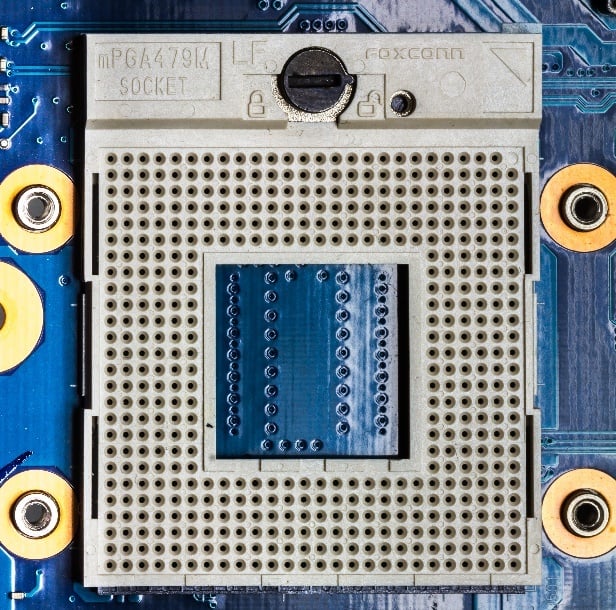
Socket 479, Image-Source: Wikipedia
A socket or a slot is usually a combination of mechanical and electrical parts that connect a microprocessor to a circuit board (motherboards in the case of PCs). Thanks to these sockets, we can easily drop in a (compatible) CPU upgrade into the same motherboard.
Now, there are several types of these CPU sockets, each with its own distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s go over the ones you’ll find on Desktop PCs.
LGA vs. PGA
When it comes to modern desktop computers, we focus on two types of sockets – LGA and PGA. You can think of them as opposites of each other.
There is another type of socket, too – BGA (Ball Grid Array), but it’s not very relevant to modern desktop computing and PC building, so I won’t be covering them.
LGA (Land Grid Array)
In recent years, Intel has become known for this type of socket. You might have heard of Intel Core processors and Intel motherboards coming with sockets like LGA 1156, LGA 1200, LGA 2011, and so on.
So, what does LGA or Land Grid Array mean? It is the name given to one type of surface-mounting packaging for Integrated Circuits (ICs). In this socket, pins are placed on the motherboard socket rather than on the chips. Consequently, LGA processors look something like this:
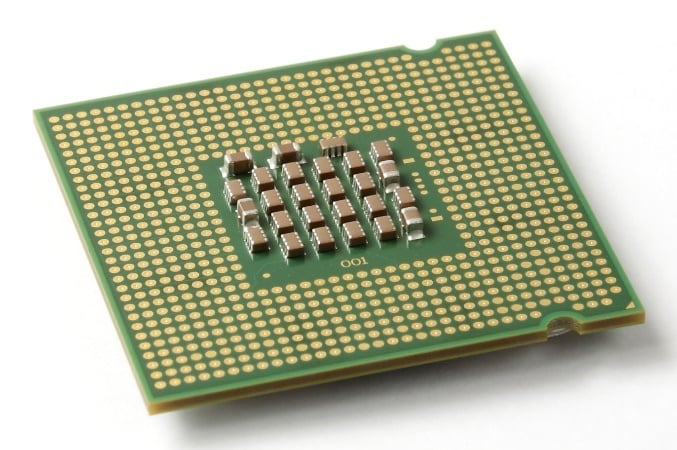
CPU – Image-Source: Wikipedia
LGA 775 Intel Pentium 4 Prescott CPU (Wikimedia)
Notice how there are only flat gold contacts on the chip? No pins.
The pins are housed on the motherboard instead.
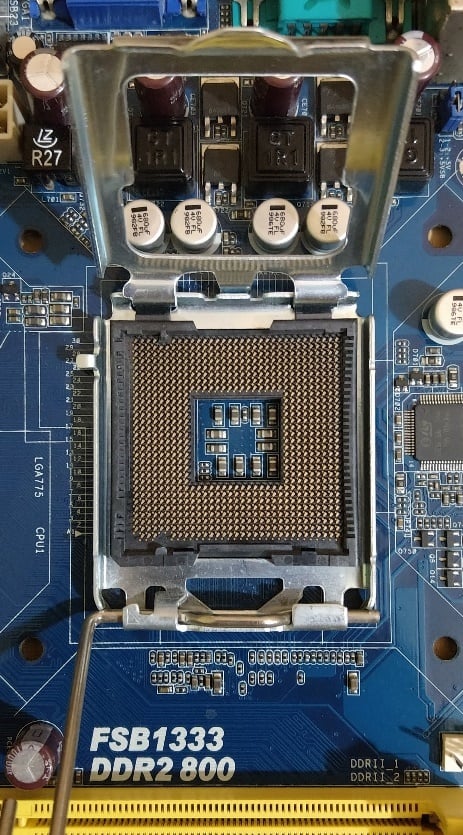
LGA 775 Socket – Image-Source: Wikipedia
Many say that an LGA socket is ‘safer’ because you can’t damage your CPU pins this way. However, as someone who has managed to drop their Intel CPU on its edge right into an LGA socket, I can tell you – only the location of the damage changes if you’re a klutz like me.
That said, I guess the processor is usually the more expensive part, so better you damage a motherboard rather than damage CPUs?
PGA (Pin Grid Array)
The Pin Grid Array or PGA has become an AMD hallmark (even though their HEDT platform does use LGA sockets), thanks to its extensive use on their consumer platforms. Even their newest generation of Ryzen processors’ socket, AM4, is PGA.
You can think of PGA as the opposite of an LGA socket, i.e., pins are on the processor chip.
Here’s what a PGA processor looks like:
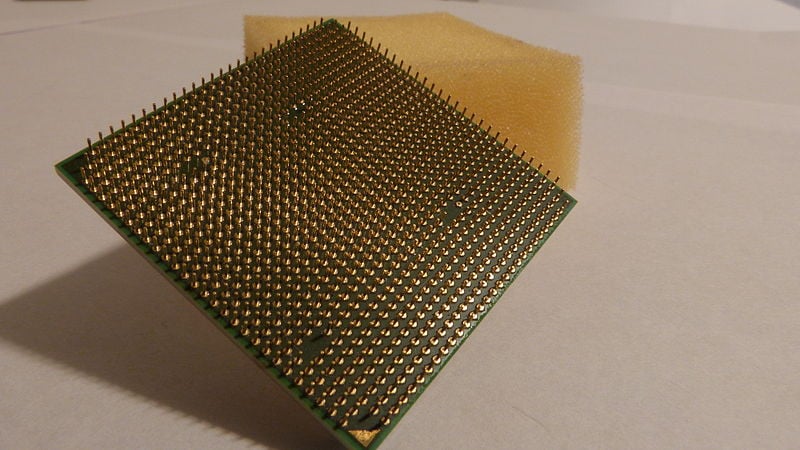
PGA AM2+ AMD Phenom X4 9750 CPU (Wikimedia)
As you can see, all the pins are on the processor chip. On the other hand, a PGA socket on the motherboard looks like this:
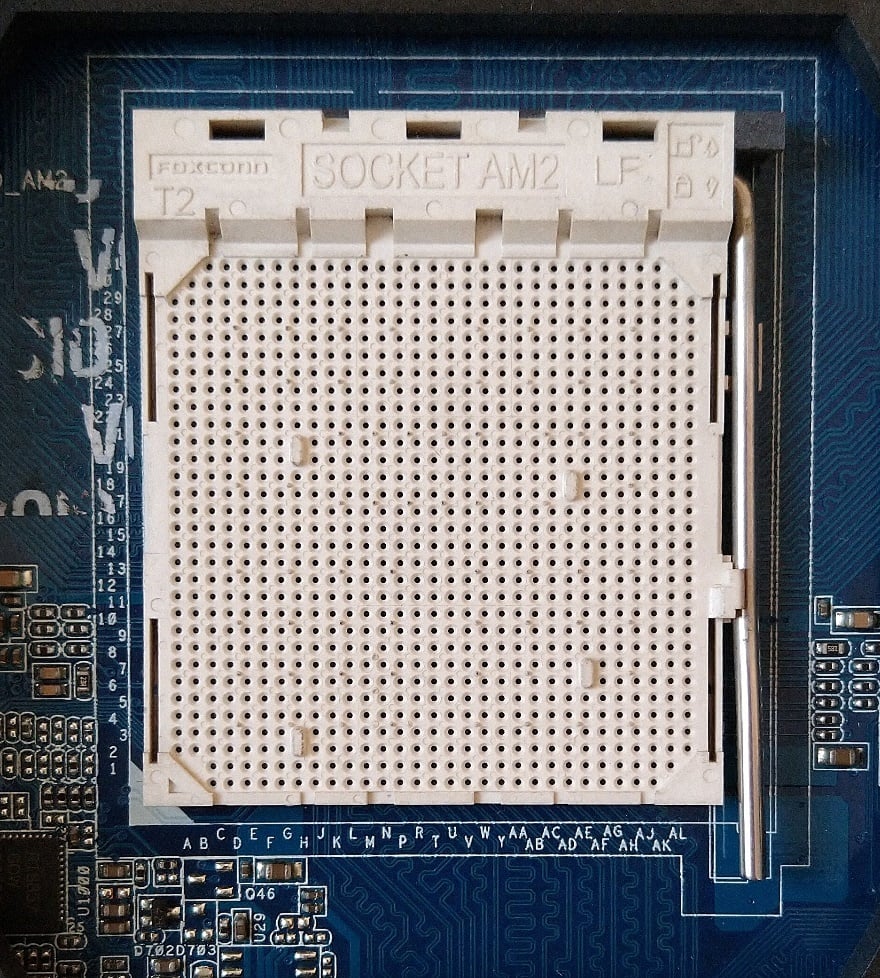
PGA AM2+ Socket on Motherboard (Wikipedia)
An easy way to recall what kind of processors LGA and PGA indicate is by using their names – Land Grid Array and Pin Grid Array.
LGA – Land, i.e., Flat CPU with no pins, motherboard sockets with pins.
PGA – Pins, i.e., Not Flat – CPUs with pins, Motherboard sockets without pins.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which is Better – LGA or PGA?
There’s really no right answer to this one. Both have their advantages and disadvantages. Personally, I prefer PGA because I find it easier to fix pins on a CPU than attempting to straighten out a motherboard’s LGA pins. However, many prefer the latter, so it usually comes down to preference.
That said, LGA does have advantages like more pin count and higher power delivery, so manufacturers won’t shy away from using them when needed (probably even AMD one day down the line).
LGA vs. PGA vs. BGA?
If you’ve been reading about sockets, you would also have stumbled upon another type – BGA. BGA, or Ball Grid Array, is another type of surface package mounting.
Here, small ‘balls’ of solder element are placed between the CPU and small copper contacts inside the motherboard socket. The resulting part is then treated with an infrared iron or an oven, so the solder balls melt and attach the CPU to the motherboard.
However, unlike PGA and LGA, BGA is permanent, i.e., a CPU once installed on that motherboard cannot be swapped out. You’ll find extensive use of BGA in devices like smartphones and laptops.
Is AMD LGA or PGA?
Well, it depends. As of 2021, AMD’s mainstream Ryzen CPUs are PGA, while its HEDT lineup (Threadripper) is LGA.

![How to Get a CPU Cooler off of a CPU [Un-stick Glued-On Cooler] How to Get a CPU Cooler off of a CPU [Un-stick Glued-On Cooler]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/03/How-to-get-CPU-Cooler-off-CPU-Twitter-copy-594x335.jpg)

![“Best” PC Bottleneck Calculators [CPU/GPU]: Do they even work? “Best” PC Bottleneck Calculators [CPU/GPU]: Do they even work?](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2024/01/Best-PC-Bottleneck-Calculators-CPUGPU-Explained-Twitter-594x335.jpg)
![Best CPU for Video Encoding [2024 Update] Best CPU for Video Encoding [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2022/02/Best-CPU-For-Video-Encoding-Twitter-594x335.jpg)

3 Comments
22 April, 2023
YOU ARE A GENIUS . THANKS MUCH. YOU ARTICLE ON LGA AND PGA HAS HELPED ME CLEAR ALL CONFUSION ONCE AND FOR ALL REGARDING SUCKETS AND CPUs
17 February, 2023
I would like to know what actually is build under processor socket which is able to attract both processors to execute it functions
I’m wondering always
3 March, 2023
Hey Adu,
I’m not entirely sure what you’re asking, but if it’s how a CPU is capable of “thinking” or calculating stuff, then this book will surely help you:
https://www.amazon.com/But-How-Know-Principles-Computers-ebook/dp/B00F25LEVC
Cheers,
Alex